Ultra Wideband / UWB
What is it exactly? UWB (also called Ultra Wideband) is a digital wireless technology for close range. It is based on very high frequencies that provide spatial and directional data. With UWB, objects can be located with an accuracy of up to 10 cm. This means that the robust wireless technology with its long range is optimally designed for the shop floor.
What are the origins of UWB?
The origins of UWB date back to the 1880s when Heinrich Hertz invented the spark-gap transmitter and Guglielmo Marconi improved it to send the first radio transmission across the Atlantic. The pulse-based broadband radio technology RADAR was used during World War II to determine the distance, angle and speed of objects. Seven decades later, UWB is providing location data for iPhone 11 users. But not only in consumer electronics: Recent market growth figures show a steep increase in the success of ultra wideband in Industry 4.0 applications as well. The technology is well on its way to becoming a global standard. In recent years, UWB has established itself as a key wireless technology for precise indoor positioning and location-based services in industrial environments.
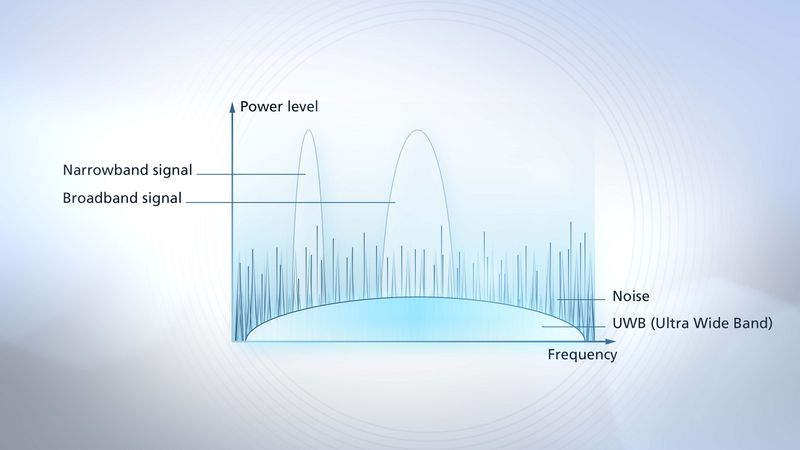
What is the difference between narrowband, wideband and ultra wideband?
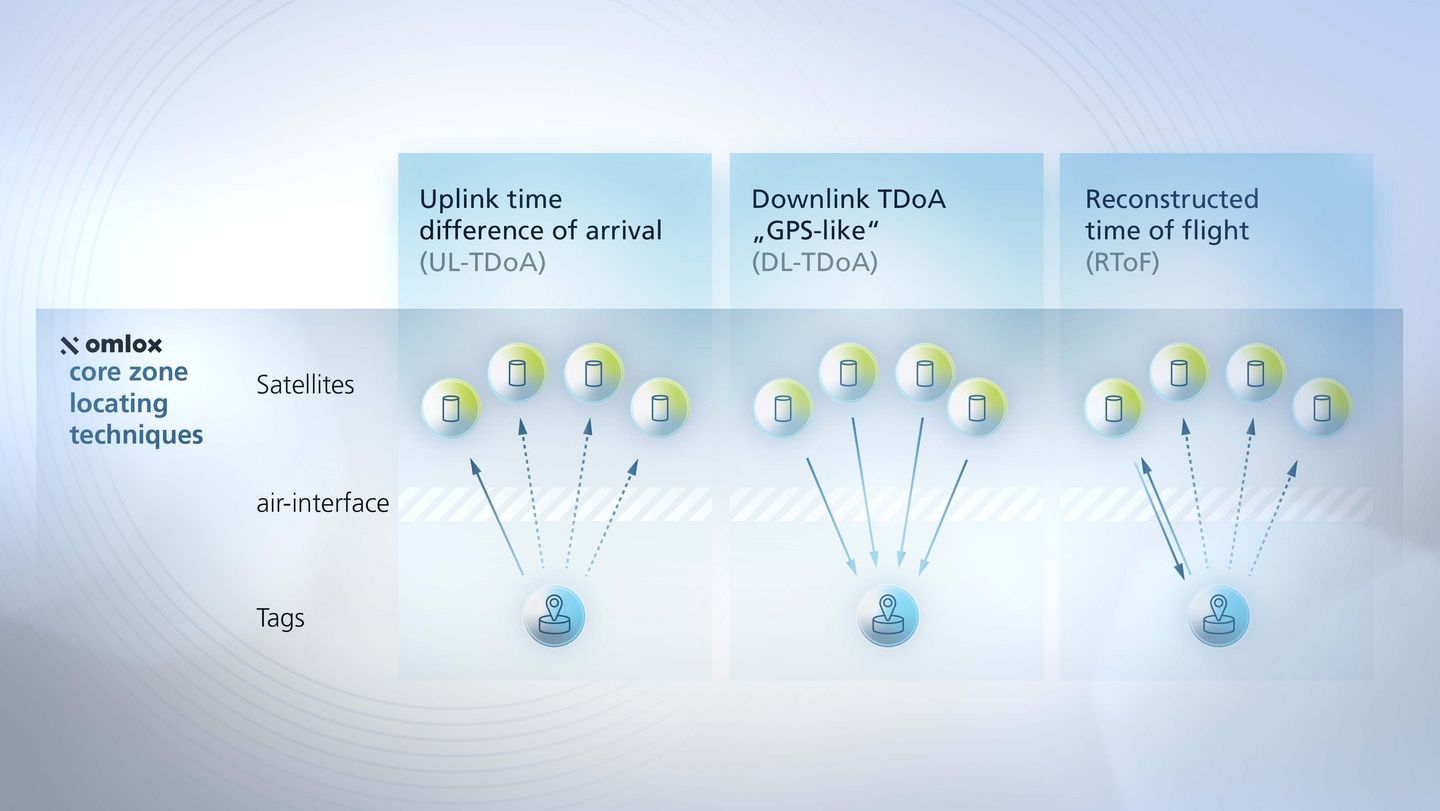
Which measurement methods for localisation are possible with omlox?
What applications are possible with UWB?
Thanks to precise location data, high temporal resolution and robust signal transmission, UWB wireless technology has proven to be clearly superior to alternative location technologies for numerous applications in the manufacturing and logistics environment.
1. Asset Tracking
With Asset Tracking, users can track the utilisation of machines/AGVs and access historic transport data and tracks. Users can thus increase productivity and improve capacity utilisation.
2. Automated Booking
Using triggers and based on geofences, certain events such as automated booking can be activated. In this way, orders can be booked automatically as soon as they reach a corresponding zone or intralogistics employees are automatically prioritised. This increases productivity while reducing waste, paving the way to a paperless factory.
3. Machine Navigation (AGV)
AGVs can increase and decrease speed based on the distances to employees, for example in order to ensure greater safety on the shop floor.
4. Human Navigation (VR)
Navigation using AR reduces the requirements for employees and makes it easier to find parts and items. The advantage: less training required for employees and a boost in productivity.
5. Automated Documentation
Automated documentation makes it possible to automate inventory of equipment and machines. Time and location data of service missions as well as machine adjustments and updates are also documented.
6. Movement Analysis
View and analyse all movements on the shop floor. This increases transparency in your factory and allows you to identify optimisation potential.
Get in touch with our experts!
Would you like to know more about how UWB can be used in manufacturing or logistics? Simply reach out to us!
How omlox enables the interoperability of different devices in UWB-based real-time location systems.